This article describes the analytic functions in Exasol.
Analytic functions perform computations on a window of rows defined by the over_clause. In contrast to GROUP BY, they compute the result for each row of the result set.
Over Clause
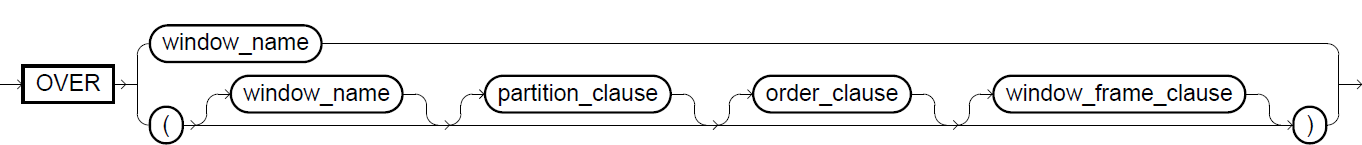
The over_clause is used to break up the data in a query into partitions and to determine the order in which the partitions are processed. The over_clause may contain a partition_clause, an order_clause, and a window_frame_clause.
Partition Clause
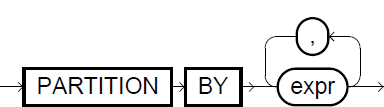
The partition_clause defines expressions that Exasol uses to partition the result set. To compute the result for a row, the function operates only on the rows in the partition containing the current row. Without the partition_clause, Exasol treats the entire result set as a single partition. If the query does not specify an order_clause nor a window_frame_clause, the default window_frame_clause is ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING.
Order Clause
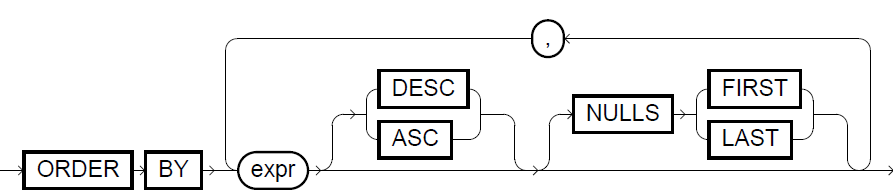
The order_clause specifies the ordering of the data within each partition. If the analytic function contains an order_clause but not a window_frame_clause, the default window_frame_clause is RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW. If the analytic function does not contain an order_clause, Exasol does not sort the data within each partition. Without sorted data, the use of some analytic functions can cause non-deterministic results.
Window Frame Clause
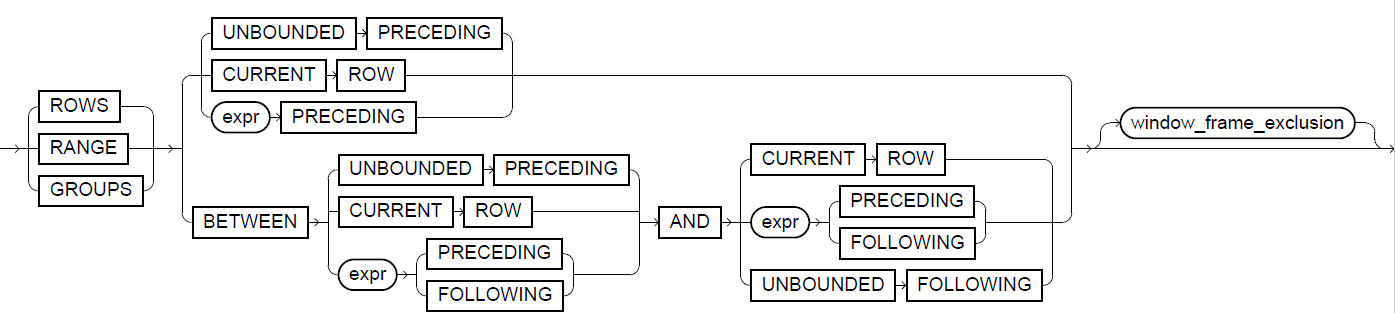
The window_frame_clause defines a window of rows that Exasol uses as input for computing the analytic function. The window can be specified for each row in terms of window_frame_units relative to the current row and within the partition to which the current row belongs. Exasol supports following window_frame_units:
- Number of rows
For example,
ROWS BETWEEN 5 PRECEDING AND 5 FOLLOWING,ROWS BETWEEN column_A PRECEDING AND column_B FOLLOWING - Range of order values relative to the order value in the current row
For example,
RANGE BETWEEN 5 PRECEDING AND 5 FOLLOWING,RANGE BETWEEN column_A PRECEDING AND column_B FOLLOWING - Number of groups of peer rows. Rows with the same order value are called peer rows
For example,
GROUPS BETWEEN 5 PRECEDING AND 5 FOLLOWING,GROUPS BETWEEN column_A PRECEDING AND column_B FOLLOWING
Additionally, it is possible to use UNBOUNDED PRECEDING, CURRENT ROW, and UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING clauses to specify the window boundaries.
Exasol also supports a short form for window frames that use CURRENT ROW. For example, RANGE UNBOUNDED PRECEDING is equivalent to RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW.
For ROWS or GROUPS, the computed expr in expr PRECEDING or expr FOLLOWING has to be a numeric value greater or equal 0 with scale 0. For RANGE the computed expr in expr PRECEDING or expr FOLLOWING has to be a numeric (or interval) value greater or equal 0.
The following example shows the different results by using window_frame_units:
SELECT
part, ord, arg,
LISTAGG(arg, ',') OVER (PARTITION BY part ORDER BY ord ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING) LISTAGG_ROWS,
LISTAGG(arg, ',') OVER (PARTITION BY part ORDER BY ord RANGE BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING) LISTAGG_RANGE,
LISTAGG(arg, ',') OVER (PARTITION BY part ORDER BY ord GROUPS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING) LISTAGG_GROUPS
FROM ex_table ORDER BY part, ord;Result
| PART | ORD | ARG | LISTAGG_ROWS | LISTAGG_RANGE | LISTAGG_GROUPS |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,2 | 1,2 | 1,2 |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 1,2,3 | 1,2 | 1,2,3,4 |
| 1 | 5 | 3 | 2,3,4 | 3,4,5 | 2,3,4,5 |
| 1 | 5 | 4 | 3,4,5 | 3,4,5 | 2,3,4,5 |
| 1 | 6 | 5 | 4,5 | 3,4,5 | 3,4,5 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1,2 | 1 | 1,2,3 |
| 2 | 5 | 2 | 1,2,3 | 2,3,4 | 1,2,3,4 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 2,3,4 | 2,3,4 | 1,2,3,4 |
| 2 | 6 | 4 | 3,4 | 2,3,4 | 2,3,4 |
Window Frame Exclusion Clause
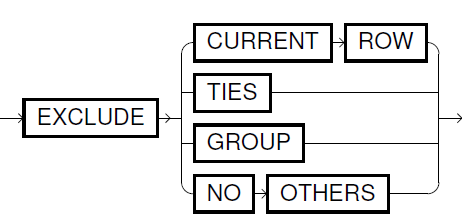
The window_frame_clause may also contain the window_frame_exclusion clause, which makes it possible to exclude certain rows from the window before the computation of the analytic function.
| Exclusion Clause | Description |
|---|---|
EXCLUDE CURRENT ROW
|
Excludes the current row |
EXCLUDE GROUP
|
Excludes the group of peer rows (rows with same order value) of the current row |
EXCLUDE TIES
|
Excludes the group of peer rows, but keeps the current row in the window |
EXCLUDE NO OTHERS
|
Does not exclude any row from the window |
If the query does not contain a window_frame_exclusion clause, the default behavior is EXCLUDE NO OTHERS.
Named Window Clause
The window clause allows the definition of named window specifications (i.e., the content of over_clauses) for analytic functions. It allows the association of identifiers (i.e., a window_name) with a specification. By referencing the identifier in the over_clause it is possible to use the same specification several times in a single statement. This shortens the SQL query and increases its readability. Additionally, it is possible to combine named window specifications with each other.
The following example shows the different results by using a named window clause:
SELECT
id, department, hire_date, starting_salary,
AVG(starting_salary) OVER w2 AVG,
MIN(starting_salary) OVER w2 MIN_STARTING_SALARY,
MAX(starting_salary) OVER (w1 ORDER BY hire_date)
FROM employee_table
WINDOW w1 as (PARTITION BY department), w2 as (w1 ORDER BY hire_date)
ORDER BY department, hire_date;Result
| ID | DEPARTMENT | HIRE_DATE | STARTING_SALARY | AVG | MIN | MAX |
| 2005 | ACCOUNTS | 2013-01-01 | 30000 | 30000 | 30000 | 30000 |
| 2003 | ACCOUNTS | 2015-07-01 | 50000 | 40000 | 30000 | 50000 |
| 2002 | ACCOUNTS | 2017-01-01 | 40000 | 47500 | 30000 | 70000 |
| 2004 | ACCOUNTS | 2017-01-01 | 70000 | 47500 | 30000 | 70000 |
| 2001 | ACCOUNTS | 2018-07-01 | 40000 | 46000 | 30000 | 70000 |
| 1003 | HR | 2014-01-01 | 35000 | 35000 | 30000 | 35000 |
| 1002 | HR | 2016-01-0 | 45000 | 38333.333 | 30000 | 45000 |
| 1004 | HR | 2016-01-0 | 35000 | 38333.333 | 30000 | 45000 |
| 1001 | HR | 2016-01-0 | 50000 | 41250 | 30000 | 50000 |
Syntax
analytic_functions::=
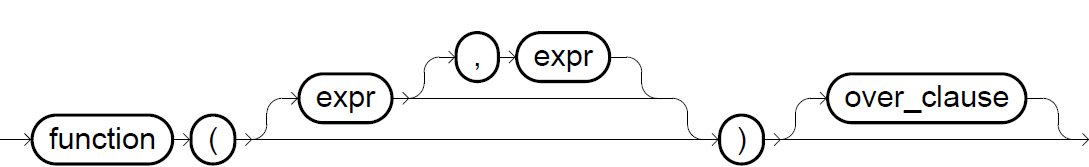
over_clause::=
partition_clause::=
order_clause::=
window_frame_clause::=
window_frame_exclusion::=
window_clause::=
Usage Notes
- Analytic functions are always evaluated after
WHERE,GROUP BY, andHAVINGclause, but before the globalORDER BYclause. - The results within each partition are computed independently from the other partitions in the result set.
- In the
window_frame_clause, the lower boundary of the window must lie before, or can be the same as the upper boundary according to the sorting order of the rows. Exasol returns an error if this condition is violated. - If the analytic function uses
DISTINCT, the function must not contain anorder_clauseand must not contain awindow_frame_clause. - The use of a non-default
window_frame_exclusionclause is only possible in combination with anorder_clause. - The use of window frame unit
RANGEin combination withexpr PRECEDINGorexpr FOLLOWINGrequires anorder_clausewith a single order expression. - Exasol allows the use of analytic functions only in the select list, in a
QUALIFYclause, or in the globalORDER BYclause. - It is possible to replace the contents of the
over_clausepartially or completely by referring to anamed_windowidentifier. To use such a window it is necessary to define the identifier and the associate window specification parts (for example, apartition_clause) in theNamed Window Clause. - Exasol does not support nested analytic functions.
- The position of the
window_clauseis afterHAVINGin aSELECTstatement. -
It is not possible to override a previously defined
window_nameidentifier. - The scope of the
window_clauseis only the currentSELECTstatement. It does not include subqueries. - It is possible to combine several named window specifications. However, the combination has to contain only one
partition_clause, oneorder_clause, and onewindow_frame_clause. -
If a named window specification contains an
order_clause, you cannot combine it with apartition_clause. -
If a named window specification contains a
window_frame_clause, you cannot combine it with any other analytic function clause.
Example:
The input table share_closing_prices in the example lists closing prices of shares of different companies over 10 days. The following query generates a moving average of the closing price for each share for the previous 4 days and the current day.
SELECT
COMPANY, TRADING_DATE, CLOSING_PRICE,
AVG(CLOSING_PRICE) over (PARTITION BY COMPANY ORDER BY TRADING_DATE ROWS BETWEEN 4 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) MOVING_AVG
FROM shares_closing_prices;Result
| Company | TRADING_DATE | CLOSING_PRICE | MOVING_AVG |
| AAPL | 2018-12-17 | 163.94 | 163.94 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-18 | 166.07 | 165.005 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-19 | 160.89 | 163.63333 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-20 | 156.83 | 161.9325 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-21 | 150.73 | 159.692 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-24 | 146.83 | 156.27 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-26 | 157.17 | 154.49 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-27 | 156.15 | 153.542 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-28 | 156.23 | 153.422 |
| AAPL | 2018-12-31 | 157.74 | 154.824 |
| INTC | 2018-12-17 | 47.08 | 47.08 |
| INTC | 2018-12-18 | 47.74 | 47.41 |
| INTC | 2018-12-19 | 45.57 | 46.796667 |
| INTC | 2018-12-20 | 45.54 | 46.4825 |
| INTC | 2018-12-21 | 44.84 | 46.154 |
| INTC | 2018-12-24 | 43.59 | 45.456 |
| INTC | 2018-12-26 | 46.19 | 45.146 |
| INTC | 2018-12-27 | 46.36 | 45.304 |
| INTC | 2018-12-28 | 46.75 | 45.546 |
| INTC | 2018-12-31 | 46.93 | 45.964 |
The analytic function used in this example is AVG. The query partitions the table by COMPANY and orders the data by TRADING_DATE. The result for each row is the average of the CLOSING_PRICE for previous 4 days and the current day.
Supported Analytic Functions
Exasol supports the following analytic functions:

