Get started with Lakehouse Turbo
This article explains how to sign up and get started using Lakehouse Turbo.
Introduction
You can sign up for a free trial of Lakehouse Turbo to explore the full power of the plug-and-play query engine without cost. The trial account provides all the functionality of Exasol SaaS for a limited time. After the trial period ends, you will be charged monthly for the subscription.
This article explains how to sign up and get started with the Lakehouse Turbo trial. You can also enable Lakehouse Turbo for a new database in an existing Exasol SaaS account. In that case, skip the first step and go directly to Step 2: Add a database.
Prerequisites
-
An active Databricks account
-
Access to the AWS account that hosts the S3 bucket for the data lakehouse
-
Permissions to grant Lakehouse Turbo access to the S3 bucket
Step 1: Sign up
Sign up for your free trial account on https://cloud.exasol.com/lakehouse-turbo-signup. You will receive a verification email with instructions on how to set up your account and create a secure password. After setting up your account, you will receive another email with your account details and can sign in.
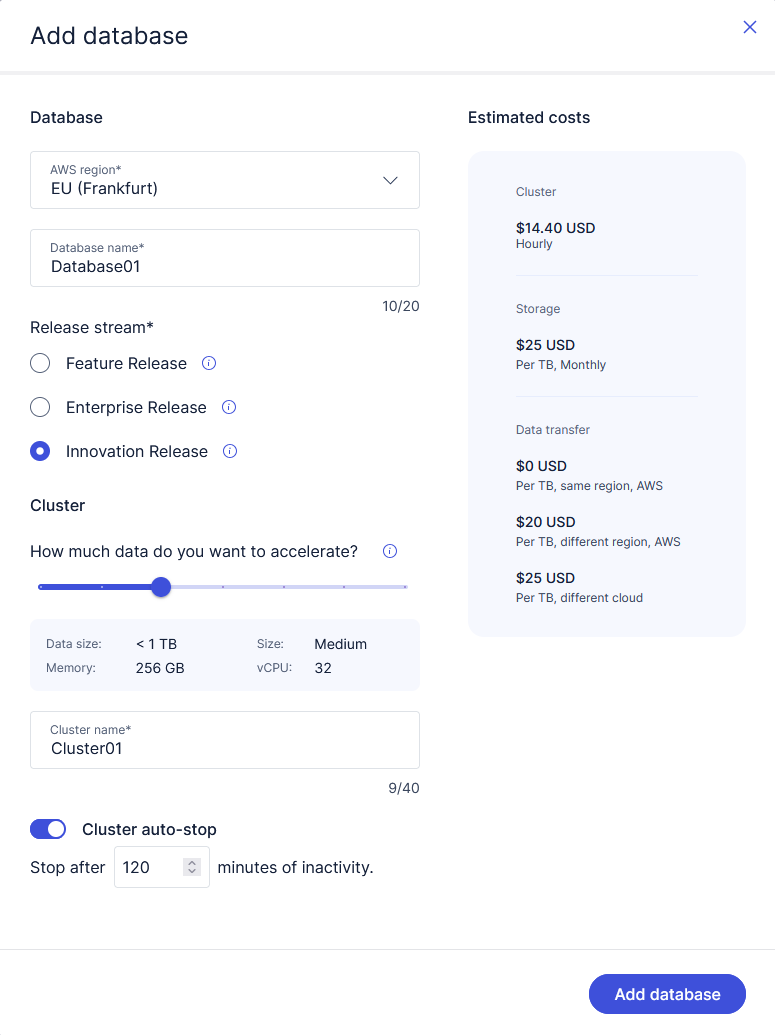
Step 2: Add a database
The first time you sign in, you will be asked to add a new database. If you are already signed in to Exasol SaaS, you can add a new database from the Databases page.
-
Select the AWS region where the new database should be deployed.
To avoid cross-region data transfer costs, always select the AWS region where the S3 bucket of your Data Lake is deployed.
-
Enter a name for the database.
-
Select Innovation Release as the release stream. Lakehouse Turbo is not supported in the Feature and Enterprise release streams.
-
Choose a cluster size based on the amount of data to be mirrored in Lakehouse Turbo.
-
Select a timeout value for the Cluster auto-stop feature, which automatically stops the cluster after a period of inactivity. The default value is 120 minutes. You can also disable the auto-stop feature.
Disabling the auto-stop feature may result in increased cloud resource usage.
Example:
When you have finished setting the options for your database, click on Add database.
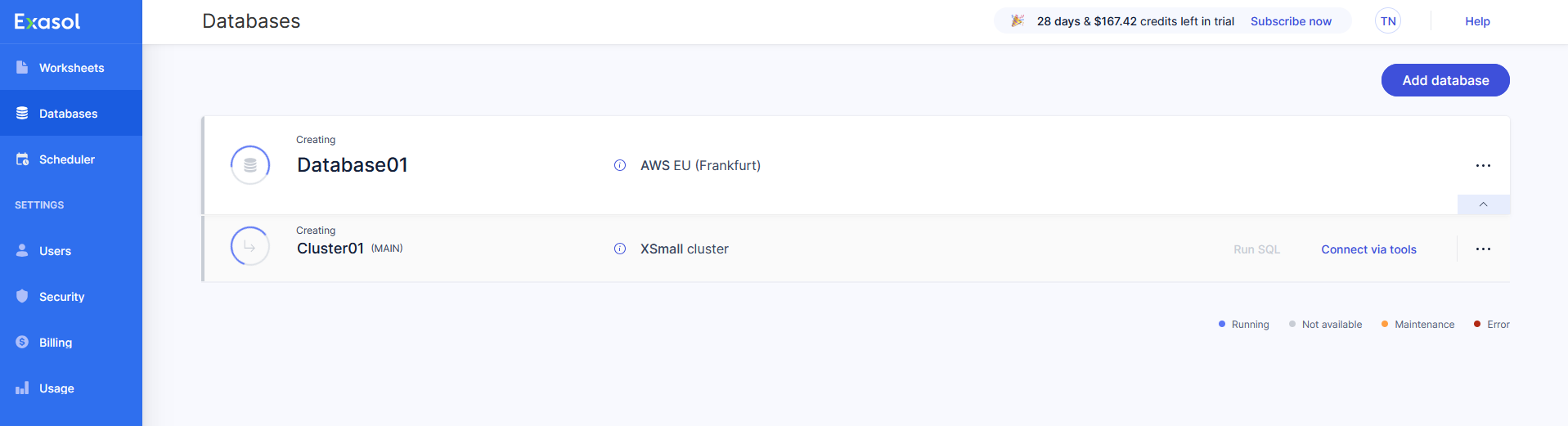
On the Databases page, the new database and cluster will have the status Creating until they are ready for use. The creation process will take about 15 minutes to complete. You will receive an email when your database is ready for use.
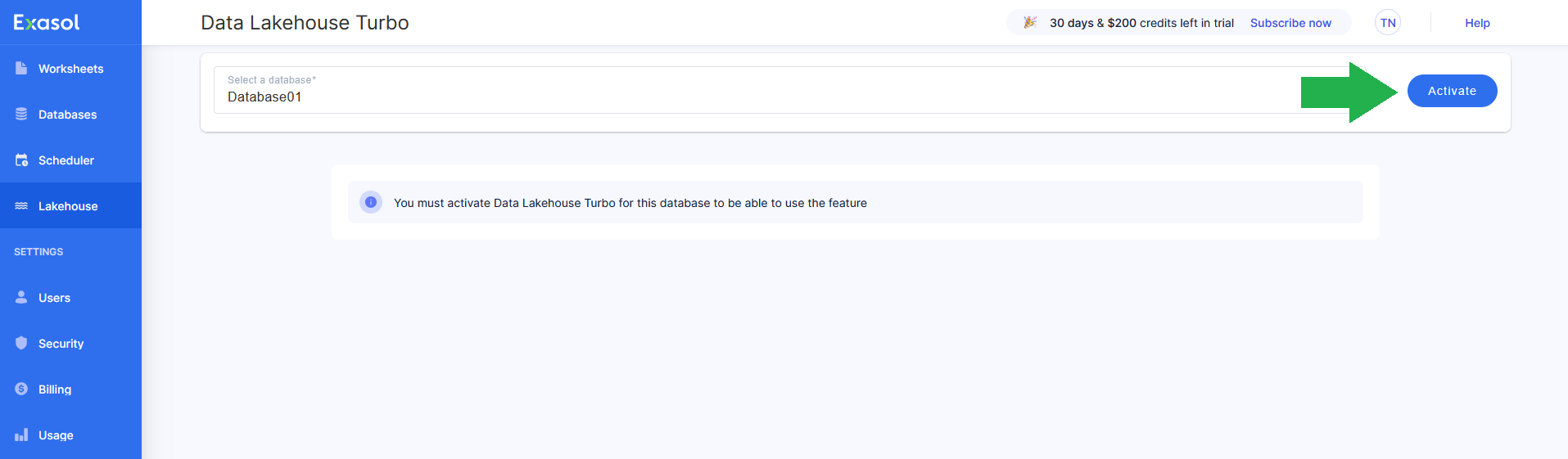
Step 3: Activate Lakehouse Turbo
When your database is up and running, go to the Lakehouse page and click on Activate to activate Lakehouse Turbo for the selected database.
Step 4: Configure the Databricks workspace
To be able to smartly mirror selected tables within Exasol, Lakehouse Turbo must be able to access the metadata and the storage layer of the data lakehouse.
This step explains how to grant Lakehouse Turbo read-only access to the following:
-
Databricks REST API via an OAuth service principal
-
The underlying S3 bucket where the data is stored
-
Create an OAuth Principal in your Databricks account
In Databricks you can add service principals either on the account level or on the workspace level. To add and configure a service principal on the account level, you must have the account admin role. To learn how to do add an OAuth service principal, see the following sections in the Databricks documentation:
Add service principals to your account (account console)
Add service principals to your account (workspace admin settings)
-
Assign the OAuth service principal to your Databricks workspace
The next step is to assign the OAuth service principal to your Databricks workspace. You can do this using either the account console or the workspace admin settings page. See the following sections in the Databricks documentation:
Assign a service principal to a workspace (account console)
Assign a service principal to a workspace (workspace admin settings)
-
Grant the following privileges to the service principal on the catalogs, schemas, or tables that should be mirrored by Lakehouse Turbo:
-
USE SCHEMA(prerequisite) -
EXECUTE(read) -
READ VOLUME(read) -
SELECT(read)
-
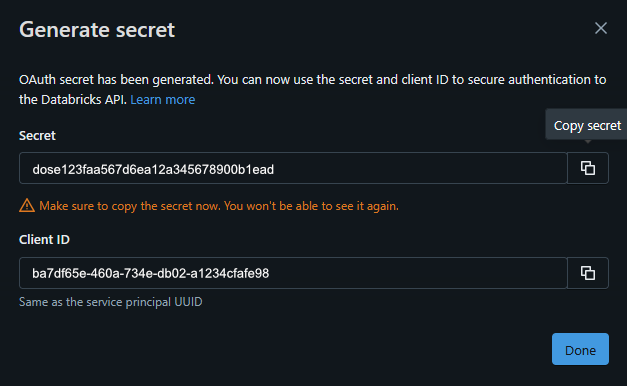
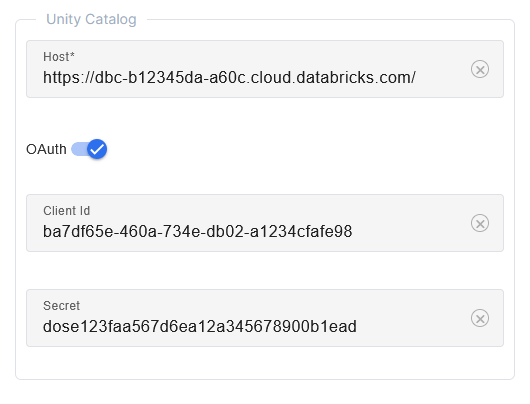
Step 5: Configure OAuth in Lakehouse Turbo
In the Lakehouse Turbo Settings tab, add the following in the Unity Catalog section:
-
The URL of the Databricks workspace host
-
The Client ID of the OAuth service principal
-
The Secret of the OAuth service principal
Example:
Step 6: Configure access to the S3 bucket
Lakehouse Turbo requires read-only access to the S3 bucket that contains the storage layer of the data lakehouse. To get access, Lakehouse Turbo will transparently assume an IAM role in your AWS account.
-
Get prerequisites
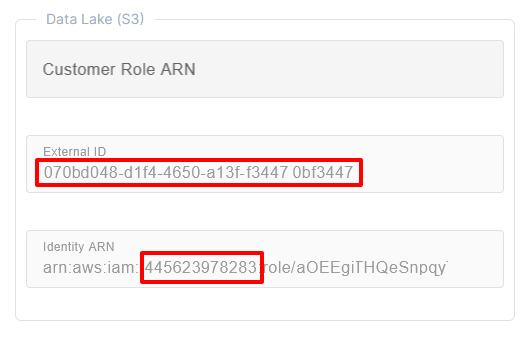
You first need to get the AWS account ID and the External ID of your Lakehouse Turbo deployment.
On the Settings tab, copy the contents of the External ID field and the the 12-digit AWS Account ID from the Identity ARN field.
Example:
-
Create IAM role in AWS
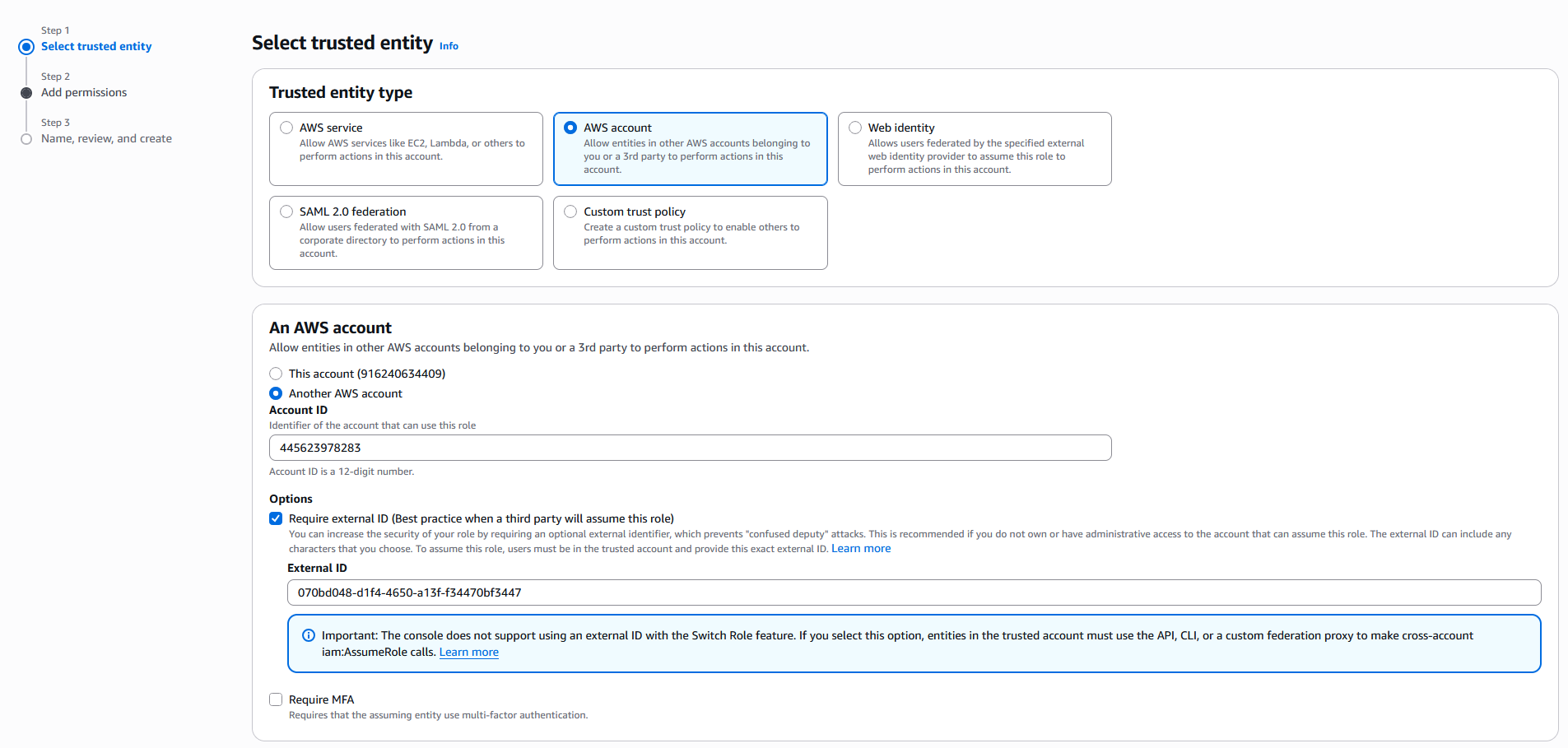
In the AWS account that hosts the S3 bucket of the data lakehouse, navigate to IAM and create a new role with the following settings:
-
Trusted entity type = AWS Account
-
Another AWS Account -> Account ID = AWS Account ID copied from the Lakehouse Turbo Settings tab (see previous step)
-
External ID = External ID copied from the Lakehouse Turbo Settings tab
Example:
Add the permission policy
AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess
. If desired, set a permissions boundary to limit access to the S3 bucket.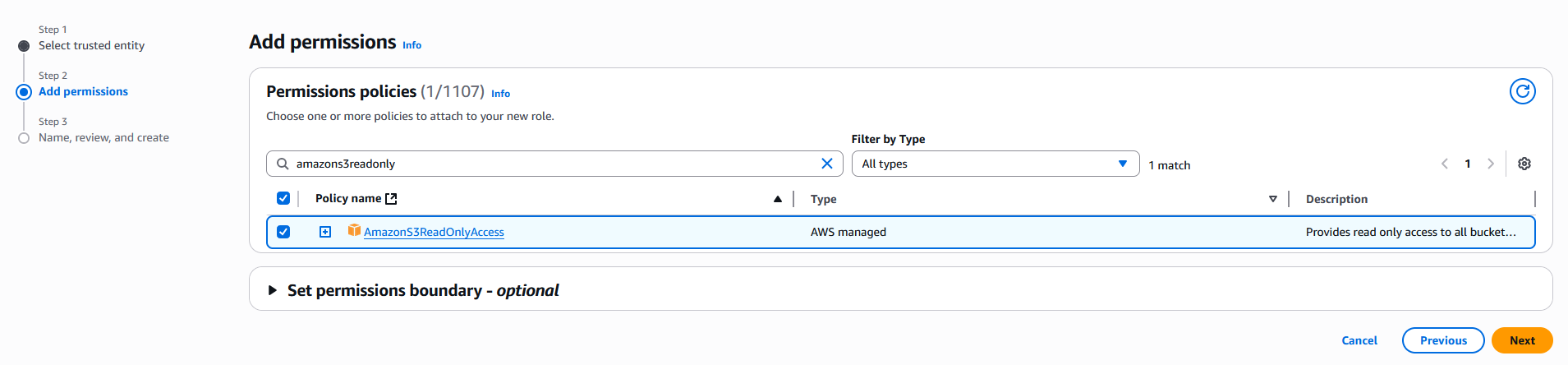
Click on Next, review the settings and add a name and description for the role, then click on Create role.
-
-
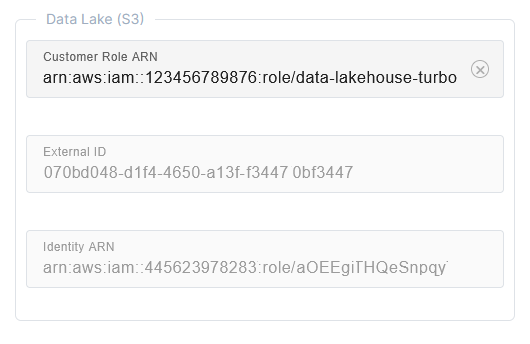
Add the Customer Role ARN in Lakehouse Turbo
In the Lakehouse Turbo Settings tab, enter the ARN of the newly created role in the Customer Role ARN field in the Data Lake (S3) section.
Example:
-
Optional - Grant access to the role within S3
This step is only required if the created IAM role is in a different AWS account than the S3 bucket.
In the AWS account that hosts the S3 bucket of the data lakehouse, navigate to S3 and do the following:
-
Locate the S3 bucket of your datalake
-
Click on the bucket name and navigate to the Permissions tab
-
Create the role and copy the ARN of the role
-
Add the following statement to the Bucket policy:
Copy{
"Sid": "Grant access for Data Lakehouse Turbo",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "${ROLE_ARN}"
},
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"${BUCKET_ARN}/*",
"${BUCKET_ARN}"
]
}
-
Next steps
Once you have connected to your data lakehouse, the next step is to select the catalog and schemas that you want to accelerate using the smart caching in Lakehouse Turbo.