Upload TLS certificate
This article explains how to create a TLS certificate chain and upload it to your Exasol system.
Introduction
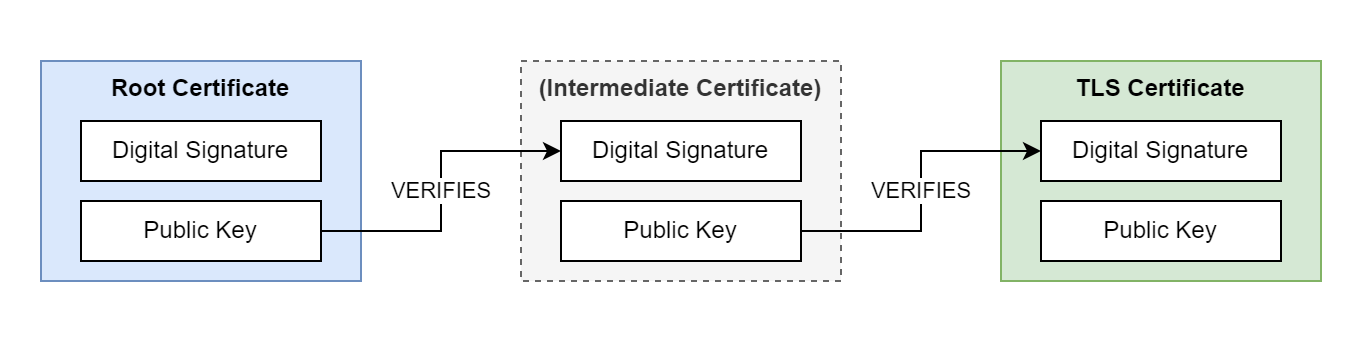
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol that uses digital certificate chains to enable secure communication between client and server. A certificate chain consists of multiple, related certificates that are linked together using digital signatures. Each certificate in the chain is digitally signed by the previous certificate in the chain. The root certificate in the chain can be self-signed or issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). The certificate chain can contain any number of intermediate certificates between the root and server certificates.
TLS certificates are used to encrypt communication between an Exasol system and the different administration tools, for accessing the database from a database client, and for accessing BucketFS. You can upload the certificate chain to the Exasol system using ConfD.
If you need help on how to generate or use TLS certificates, contact your system administrator.
Prerequisites
- A self-signed or CA-signed server certificate using either RSA or ECC encryption
-
A private key file for the server certificate
-
The root certificate and any intermediate certificates that are part of the certificate chain
The maximum length of the private key is 8192 bits.
The private key for the server certificate must not be encrypted with a password.
Create a certificate chain
A certificate chain is a simple text file that contains all the certificates. The ordering of the certificates in the file is important. Certificate chains begin with the server certificate and end with the root certificate. In the following example we use the cat command to create a certificate chain file that contains two certificates.
-
Copy the server certificate
server_cert.crt
to a new certificate chain filecert_chain.pem
.Copycat server_cert.crt > cert_chain.pem; -
Append the CA-issued root certificate
ca_cert.crt
to the file.Copycat ca_cert.crt >> cert_chain.pemNote that you must use
>>(append), not>(overwrite) in this step.
The file cert_chain.pem
now contains a certificate chain with a server certificate and a root certificate. The next step is to upload this file to the Exasol system together with the private key for the server certificate.
Hostnames in the server certificate
If the SQL driver is using a connection string in the format first_host..last_host:port, the exact hostnames provided in the connection string must be included in the Common Name (CN) or Subject Alternative Name (SAN) of the server certificate.
Example:
|
Driver connection string |
Include in server certificate |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
or
|
|
|
exa-prod.mydomain
or
|
Upload certificate and key
The next step is to upload the certificate chain and the private key to the Exasol deployment.
You must upload the entire TLS certificate chain, not just the server certificate.
This procedure is carried out using ConfD and Exasol Deployment Tool (c4).
-
Copy the certificate chain and the private key from your local system to the cluster operating system (COS) on one of the cluster nodes. To do this, you can use the following single-line command that creates a tarball of the two files, connects to COS on the node using
c4 connect -i <PLAY_ID> -n <NODE> -s cos, and then copies and extracts the archive in the COS container. You can use any active node in the cluster.Replace the play ID
c3275f84and the node ID11in the following examples with the actual IDs from your deployment.Copytar cf - cert_chain.pem key.pem | c4 connect -i c3275f84 -n 11 -s cos tar xvf - -
Connect to the cluster operating system (COS) using
c4 connect -i PLAY_ID -s cos.Example:
Copy./c4 connect -i c3275f84 -s cosTo find the play ID, you can use
c4 ps.For more information about how to use c4 commands, see How to use c4.
-
Upload the certificate chain and the private key using the ConfD job cert_update.
Copyconfd_client cert_update cert: '"{< ./cert_chain.pem}"' key: '"{< ./key.pem}"'
To learn more about how to use c4 connect, see How to use c4.
The validity of the uploaded certificate is checked according to WebPKI and CA/B rules to ensure compatibility with most clients, but this is not a hard requirement and merely a warning. Any certificate/key pair can be used, but you must make sure that the clients trust the certificate.
You can only have one TLS certificate active at a time. Uploading a new certificate overwrites a previous TLS certificate. It is not possible to delete a certificate without replacing it.
Enable a TLS certificate
All Exasol drivers use TLS as the default cryptographic protocol for all connections. By default, each Exasol database uses a self-signed certificate for TLS encryption. If your database uses the default certificate or another self-signed certificate, you may need to update your connection strings to connect to the database.
SQL connections that are established after a new certificate and key have been uploaded will automatically use the new files for authentication. A database restart is not required unless the database has been configured to use non-default paths for certificates and keys, or if the legacy TLS library has been enabled (by setting the respective database parameters). In that case, you must restart the database after uploading the files.
Restarting the cluster requires a short downtime.
Fingerprint
For clients that do not support certificate verification, you can use TLS fingerprints.
When you upload a new TLS certificate a new fingerprint is generated. This means that you must update the connection string for all incoming connections. Connection requests with invalid fingerprints are rejected.
