Purpose
Using the MERGE statement, it is possible to merge the contents of an update table into a target table. The rows of the update table determines which rows will be changed, deleted, or inserted. Therefore, the MERGE statement unites these three statements - UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT.
For example, the update table can contain the data of new customers or customers to be dropped or the change information of already existing customers. The MERGE statement can now be used to insert the new customers into the target table, delete non-valid customers, and update the changes of existing customers.
Prerequisites
-
You need either the system privilege
USE ANY SCHEMAor the object privilegeUSAGEon the target schema, or the schema must be owned by you or one of your assigned roles. - You need to have the appropriate
INSERT,DELETE, andUPDATEprivileges on the target table. - You need to have the appropriate
SELECTprivileges on the update table.
Syntax
merge::=
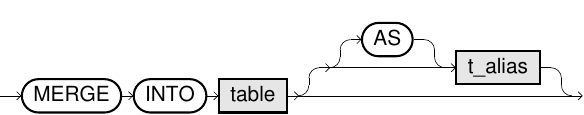
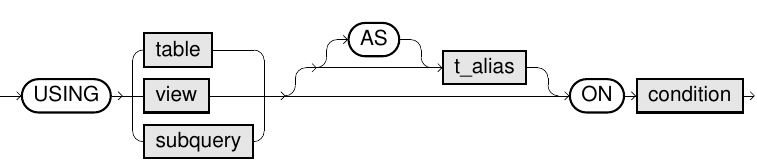
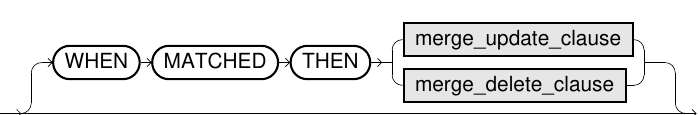

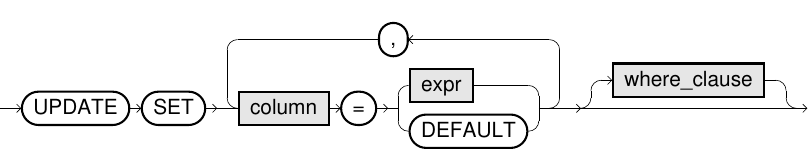
merge_update_clause::=
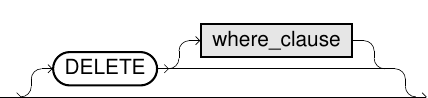
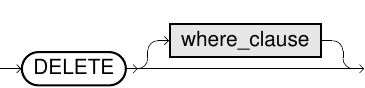
merge_delete_clause::=
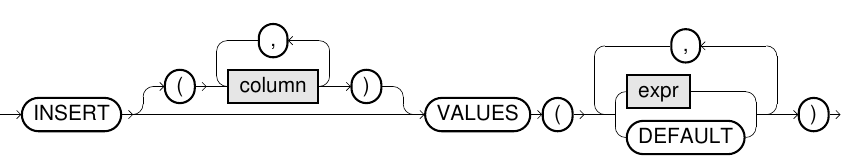
merge_insert_clause::=

Usage Notes
- The
ONcondition describes the correlation between the two tables (similar to a join). TheMATCHEDclause is used for matching row pairs, and theNOT MATCHEDclause is used for those that do not match. In theONcondition, only equivalence conditions (=) are permitted. - In the
UPDATEclause, the optionalWHEREcondition specifies the circumstances under which theUPDATEis conducted, whereby it is permissible for both the target table and the update table to be referenced for this. With the support of the optionalDELETEcondition, it is possible to delete rows in the target table. Only the rows that have been matched by theWHEREclause of theUPDATEare taken into consideration for theDELETEclause. TheWHEREclause of theDELETEstatement uses the values after theUPDATE. - In the
DELETEclause, the optionalWHEREcondition specifies the circumstances under which theDELETEis performed. - In the
INSERTclause, the optionalWHEREcondition specifies the circumstances under which theINSERTis performed. It is permissible to reference columns of the update table in theINSERTclause. - The
UPDATE,DELETE, andINSERTclauses are optional with the restriction that at least one must be specified. The order of these clauses is interchangeable. - The
INSERTandUPDATEclauses treat the default values and identity columns in the same way as in theINSERTandUPDATEstatements. However, the only exception is thatINSERT DEFAULT VALUESis not allowed. - If there are several entries in the update table that could apply to an
UPDATEof a single row in the target table, then this displays the error message "Unable to get a stable set of rows in the source tables", if theUPDATEcandidates would change the original value of the target table. - If several entries in the update table could apply to a
DELETEof a single row in the target table, this displays the error message "Unable to get a stable set of rows in the source tables".
Examples
Consider the following sample tables and examples statements based on these tables:
Staff
| name | salary | lastchange |
|---|---|---|
| meier | 30000 | 2006-01-01 |
| schmidt | 40000 | 2006-05-01 |
| mueller | 50000 | 2005-08-01 |
Changes
| name | salary |
|---|---|
| schmidt | 43000 |
| hofman | 35000 |
| meier | 29000 |
Deletes
| name |
|---|
| meier |
-- Merging the table updates
MERGE INTO staff T
USING changes U
ON T.name = U.name
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET T.salary = U.salary,
T.lastChange = CURRENT_DATE
WHERE T.salary < U.salary
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT VALUES (U.name,U.salary,CURRENT_DATE);
SELECT * FROM staff;Results
| name | salary | lastchange |
|---|---|---|
| meier | 30000 | 2006-01-01 |
| schmidt | 43000 | 2010-10-06 |
| mueller | 50000 | 2005-08-01 |
| hofmann | 35000 | 2010-10-06 |
-- Merging the table deletes
MERGE INTO staff T
USING deletes U
ON T.name = U.name
WHEN MATCHED THEN DELETE;
SELECT * FROM staff;Results
| name | salary | lastchange |
|---|---|---|
| hofmann | 35000 | 2010-10-06 |
| schmidt | 43000 | 2010-10-06 |
| mueller | 50000 | 2005-08-01 |
