Purpose
Use this statement to insert constant values as well as the result of a subquery in a table.
Prerequisites
-
You need either the system privilege
USE ANY SCHEMAor the object privilegeUSAGEon the target schema, or the schema must be owned by you or one of your assigned roles. - You need either the system privilege
INSERT ANY TABLEor the object privilegeINSERTon the table or its schema, or the table must be owned by you or one of your assigned roles. - To insert the result of a subquery, you need to have the appropriate
SELECTrights for the objects referenced in the subquery.
Syntax
insert::=
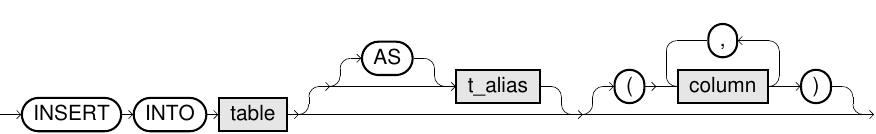
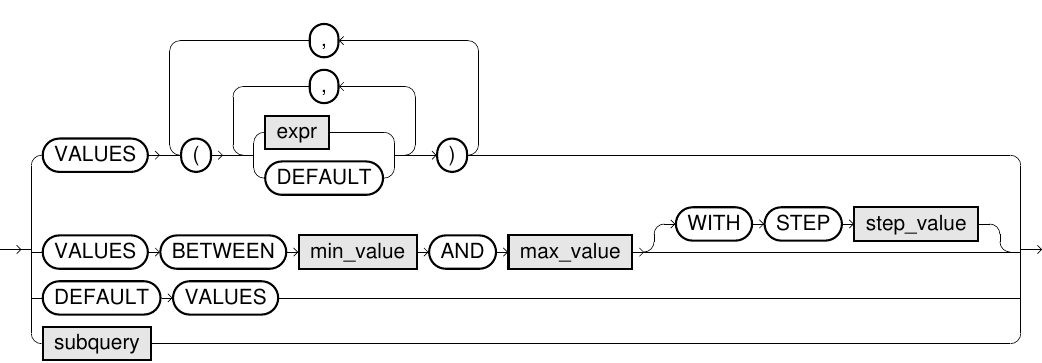
Usage Notes
- The number of target columns of the target table must match the number of constants or the number of
SELECTcolumns in a subquery. Otherwise, an exception is thrown. - If only a definite number of target columns are specified for the target table, the entries of the remaining columns will be filled automatically. For identity columns, a monotonically increasing number is
generated, and for columns with default values, their respective default value is used. For all other columns, the value
NULLis inserted. - If for
INSERT INTO t VALUESthe 'value'DEFAULTis specified for a column, then the behavior is the same as the implicit insert for unspecified columns. INSERT INTO t DEFAULT VALUEShas the same behavior as if you would specify the literalDEFAULTfor each column.- For information on default values, refer to Default values section. For information on identity columns, refer to the Identity columns section.
- For information on the syntax of subqueries, refer to the SELECT statement section under Query language (DQL).
- For information on the
VALUES BETWEENsyntax, refer to the SELECT statement.
Examples
INSERT INTO t VALUES (1, 2.34, 'abc');INSERT INTO t VALUES (2, 1.56, 'ghi'), (3, 5.92, 'pqr');INSERT INTO t VALUES (4, DEFAULT, 'xyz');INSERT INTO t (i,k) SELECT * FROM u;INSERT INTO t (i) SELECT max(j) FROM u;INSERT INTO t (i, j, k)
SELECT 5, *
FROM VALUES (2.78, 'uvw'), (8.34, 'def');INSERT INTO t DEFAULT VALUES;INSERT INTO t VALUES BETWEEN 1 AND 100;
INSERT INTO t (i) VALUES BETWEEN 1 AND 100 WITH STEP 4;