Volumes Overview
This article describes the different volume types in Exasol.
Volume types and purposes
Data in an Exasol database is stored on volumes that are assigned to storage disks.
Exasol databases have two volume types with different purposes: data volumes and archive volumes. A typical Exasol setup contains at least one data volume and one archive volume.
| Volume purpose | Volume type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Storing persistent data of a database | Data |
|
| Storing compressed backups of a database | Archive |
|
| Storing temporary data | Data |
|
When a database instance is started, Exasol automatically creates a temporary data volume for storing the temporary tablespace of the database. This volume is automatically deleted when the database is stopped.
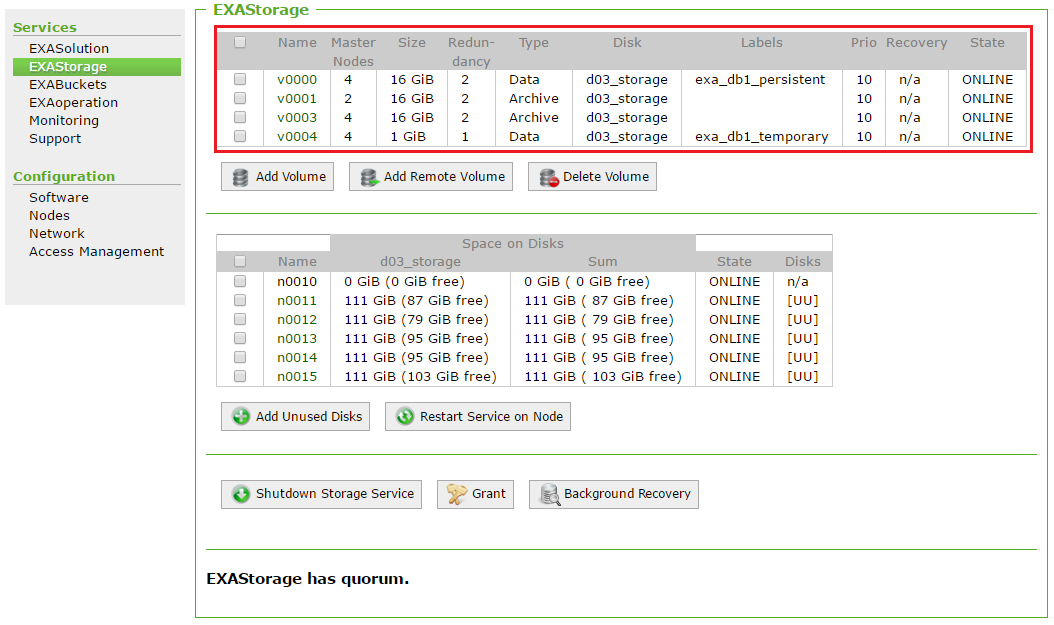
You can view the volumes in your Exasol system by going to Services > EXAStorage:
Volume nodes
When you create a persistent data volume or a local archive volume, you set the number of master nodes that the volume will use and assign them to the volume. The master nodes are the active nodes in the cluster.
For example: in a cluster that will have 4 active nodes and 1 reserve node (4+1), the number of master nodes is 4.
For persistent data volumes, the number of master nodes must match the number of active nodes you set when you create the database.
Manage volume capacity
Data volumes grow automatically as long as enough disk space is available, typically because tables grow due to insert statements.
To shrink a volume, use the action shrink on the EXASolution Instance page.