Purpose
This function computes the rank for each row by adding 1 (one) to the number of rows that precede the current row and are not peers of the current row. It implies that the rows with the same values in the ordering columns have the same rank, and there are gaps in the rank values produced by this function.
Also see DENSE_RANK function which works in a similar fashion but avoids gaps.
Syntax
rank::=
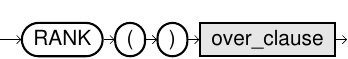
Usage Notes
RANKcan only be used as an analytic function (i.e., in combination with anover_clause). For more information, refer to Analytic functions section.- The
over_clausehas to contain anorder_clauseand must not contain awindow_frame_clause. - This function returns the same value for rows with equal ranking. Therefore, the computed results may contain gaps (as opposed to DENSE_RANK).
Example
Analytic Function
SELECT
id, department, current_salary,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY current_salary) RANK
FROM employee_table ORDER BY department, current_salary;Result
| ID | DEPARTMENT | CURRENT_SALARY | RANK |
| 2001 | ACCOUNTS | 55000 | 1 |
| 2002 | ACCOUNTS | 65000 | 2 |
| 2004 | ACCOUNTS | 70000 | 3 |
| 2003 | ACCOUNTS | 80000 | 4 |
| 2005 | ACCOUNTS | 80000 | 4 |
| 1001 | HR | 55000 | 1 |
| 1002 | HR | 70000 | 2 |
| 1004 | HR | 70000 | 2 |
| 1003 | HR | 90000 | 4 |
