Purpose
This function computes the result of expr on the row that is precisely offset rows prior to the current row in the partition.
Syntax
lag::=
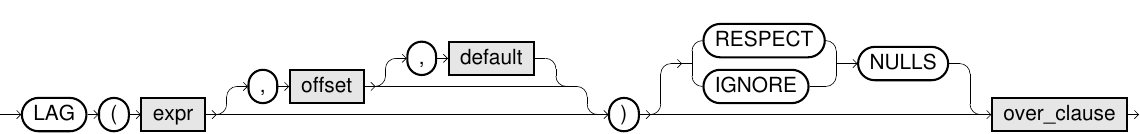
Usage Notes
LAGis only available as an analytic function (i.e., in combination with anover_clause). For more information, refer to Analytic functions section.- The
over_clausehas to contain anorder_clauseand must not contain awindow_frame_clause. - If the
order_clausedoes not define an unique sort order, the result is non-deterministic. - The
offsetparameter has to be anumericvalue greater than or equal to 0. Withoutoffset, Exasol uses the default value1. - If there are less than
offsetnumber of rows before the current row in the partition,LAGreturns thedefaultvalue for the row. Without specifieddefault, Exasol usesNULL. - If the function contains
IGNORE NULLS, Exasol skips rows withNULLduring the search for the previous row in the partition. It does not skip any rows withRESPECT NULLS. If the function contains neitherIGNORE NULLSnorRESPECT NULLSthe default isRESPECT NULLS. The use ofIGNORE NULLSis computationally more expensive thanRESPECT NULLS. - To access following rows you can use the function LEAD.
Example
Analytic Functions
SELECT
id, department, hire_date,
LAG(id, 1) OVER (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY hire_date) LAG
FROM employee_table ORDER BY department, hire_date;Result
| ID | DEPARTMENT | HIRE_DATE | LAG |
| 2005 | ACCOUNTS | 2013-01-01 | NULL |
| 2003 | ACCOUNTS | 2015-07-01 | 2005 |
| 2002 | ACCOUNTS | 2017-01-0 | 2003 |
| 2004 | ACCOUNTS | 2017-01-0 | 2002 |
| 2001 | ACCOUNTS | 2018-07-01 | 2004 |
| 1003 | HR | 2014-01-01 | NULL |
| 1002 | HR | 2016-01-01 | 1003 |
| 1004 | HR | 2016-01-01 | 1002 |
| 1001 | HR | 2018-01-01 | 1004 |
