Purpose
Use this statement to configure the current user session.
Prerequisite
None
Syntax
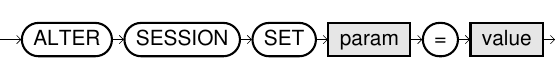
alter_session::=
Usage Notes
- The session-based parameters are initialized with the system-wide parameters (for more information, see ALTER SYSTEM). However,
you can overwrite it with the
ALTER SESSIONstatement. The current settings are available in the EXA_PARAMETERS system table. - The moment a user logs out, changes to the settings made through
ALTER SESSIONare lost. - The following table describes the parameters you can set:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
CONSTRAINT_STATE_DEFAULT
|
This parameter defines the default state of constraints ('ENABLE' or 'DISABLE') in case the state wasn't explicitly specified during the creation (see also CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE (Constraints)). |
DEFAULT_CONSUMER_GROUP
|
Specifies the default consumer groups for users and roles. For more details about consumer groups, refer to Resource Manager topic. This parameter can only be changed throughout the system using ALTER SYSTEM, but not for single sessions. However, the system-wide value is shown in the session parameter column. |
DEFAULT_LIKE_ESCAPE_CHARACTER
|
Defines the escape character for the LIKE predicate (for more details, see Predicates) if it is not specified explicitly. |
HASHTYPE_FORMAT
|
Defines the output format of data stored as HASHTYPE. The following values can be set:
The default value is UUID only works for columns with data type |
IDLE_TIMEOUT
|
Specifies a timeout in seconds. The session is killed after the specified time if there is no activity. The default value is To disable the limit, set the attribute value to
|
NICE
|
This parameter is used to reduce the priority of a session to conserve resources. The following values can be set:
For more details about priorities, see Resource Manager. |
NLS_DATE_FORMAT
|
Sets the date format used for conversions between dates and strings. For information on the possible formats, refer to the Date/time format models section. |
NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE
|
Sets the language of the date format used in abbreviated month and day formats and those written in full. Possible languages are English (ENG = Default) and German (DEU). The English language can be set using ENG or ENGLISH and the German language with DEU, DEUTSCH, and GERMAN. For more information about date/time formats, refer to the Date/time format models section. |
NLS_FIRST_DAY_OF_WEEK
|
Defines the first day of a week (integer 1-7 for Monday-Sunday). |
NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS
|
Defines the decimal and group characters used for representing numbers. This parameter is also relevant to the use of numeric format models (For more details, see Numeric format models). |
NLS_TIMESTAMP_FORMAT
|
Sets the timestamp format used for conversions between timestamps and strings. For information on the possible formats, refer to the Date/time format models section. |
PASSWORD_EXPIRY_POLICY
|
Specifies the expiry rules for user passwords. These system values can
be overwritten for single users through This parameter can only be changed throughout the system using ALTER SYSTEM, but not for single sessions. However, the system-wide value is shown in the session parameter column. |
PASSWORD_SECURITY_POLICY
|
Specifies the security rules for user passwords. For details for all the possible parameters, see Database users and roles, and Privileges. This parameter can only be changed throughout the system using ALTER SYSTEM, but not for single sessions. However, the system-wide value is shown in the session parameter column. |
PROFILE
|
Enables or disables profiling for new connections by setting the values Existing connections are not affected, only connections that are created after the |
QUERY_CACHE
|
The parameter The following values can be set:
Whether a query was returned from the cache can be determined by the
column |
QUERY_TIMEOUT
|
Defines how many seconds a statement may run before it is automatically aborted. When this point is reached, the statement may finish with an exception within a few seconds through an internal cancellation point. If this fails (for example because there are no such cancellation points or the query is slowed down due to disk operations) the query is terminated forcefully and the transaction is rolled back (including an internal reconnect). Time spent waiting for other transactions (in
state Waiting for session) is included. In case of Any changes of the
|
SCRIPT_LANGUAGES
|
Defines the script language aliases. |
|
|
Defines the hostname (or IP address) and the port number of a server to which the standard output (for example, by Python's print function) of UDF scripts are forwarded. You can deactivate the redirection of the script output by setting this parameter to the empty string. |
SESSION_TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT
|
Sets the limit for TEMP DB RAM usage by each session. If the parameter is set to OFF, no limit is applied. Users can alter this parameter for an individual session. The strictest limit will apply. The parameter must be specified as an unsigned integer, optionally followed by a single-character unit symbol M (megabytes), G (gigabytes), or T (terabytes). There must be no space between the value and the unit symbol. For example: If a unit is not specified, the value is interpreted as megabytes. Since TEMP_DB_RAM can be swapped to disk, SESSION_TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT can be set to a larger value than the DB_RAM size. |
SNAPSHOT_MODE
|
Defines the transaction Snapshot Mode for the session's connection. The possible values are:
For more information, see Snapshot Mode. |
SQL_PREPROCESSOR_SCRIPT
|
Defines a preprocessor script. If the script is specified (a regular script which was created through CREATE SCRIPT), then every executed SQL statement is preprocessed by that script. For more information on SQL preprocessing, see SQL Preprocessor. For details about the script language, see Scripting. Appropriate user privileges
must exist for executing this script.
You can deactivate the preprocessing by specifying
the empty string |
ST_MAX_DECIMAL_DIGITS
|
Defines the maximum significant digits used when casting from geometry data type to a string. You can use it to convert from geometry data type to string. It does not have any influence on the internal storage of geometry type, and on the geometry operations. The default value is 16, and the allowed range is <1,16>. For additional information, refer to the Type Conversion Rules section. |
TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT
|
Sets the limit for total TEMP DB RAM usage by all sessions. If the parameter is set to OFF, no limit is applied. This parameter can only be changed system-wide using ALTER SYSTEM, not for single sessions. However, the system-wide value is shown in the session parameter column. Since TEMP_DB_RAM can be swapped to disk, TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT can be set to a larger value than the DB_RAM size. |
TIME_ZONE
|
Defines the time zone in which the values of type |
TIME_ZONE_BEHAVIOR
|
Defines the course of action for ambiguous and invalid timestamps within a certain time zone. For more information, refer to the Date and time data types section. |
TIMESTAMP_ARITHMETIC_BEHAVIOR
|
Defines the behavior for +/- operators:
The result of subtracting two DATE values, which always results in an integer, is not changed. |
USER_TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT
|
Sets the limit for total TEMP DB RAM usage by all sessions of a user. If the parameter is set to OFF, no limit is applied. This parameter can only be changed system-wide using ALTER SYSTEM, not for single sessions. However, the system-wide value is shown in the session parameter column. Since TEMP_DB_RAM can be swapped to disk, USER_TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT can be set to a larger value than the DB_RAM size. |
Examples
ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE='EUROPE/BERLIN';ALTER SESSION SET QUERY_TIMEOUT=120;ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT='DDD-YYYY';ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE='ENG';SELECT TO_CHAR(TO_DATE('365-2007'),'DAY-DD-MONTH-YYYY') TO_CHAR1;ALTER SESSION SET NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS=',.';
SELECT TO_CHAR(123123123.45, '999G999G999D99') TO_CHAR2;ALTER SESSION SET SCRIPT_OUTPUT_ADDRESS='10.242.2.21:3000'
ALTER SESSION SET SESSION_TEMP_DB_RAM_LIMIT = '10240M';ALTER SESSION SET SNAPSHOT_MODE = 'OFF';
--or
ALTER SESSION SET SNAPSHOT_MODE = 'SYSTEM TABLES';ALTER SESSION SET IDLE_TIMEOUT = 2400;