This article describes how to ensure business continuity using dual data centers.
To ensure database availability in case of a data center outage you can implement a solution with two data centers in order to reduce downtime and protect your data. The data centers can, for example, be located in two different fire zones in the same building. This article is an overview of the different dual data center solutions you can use with Exasol.
ETL based solution
In an ETL based dual data center solution each data center has an autonomous cluster with an autonomous database. Both databases can be used simultaneously, and business critical data is replicated regularly between them using an ETL approach. If one of the data centers has an outage, the connections are redirected to the database in the other data center.
-
RTO (recovery time objective) is less than one hour.
-
RPO (recovery point objective) depends on the ETL frequency – everything changed after the last ETL replication will be lost.
Backup based solutions
In a backup based dual data center solution, backups of the production database made in one data center are available for the second data center in case the first data center has an outage. A restore on the second site makes the production database available again.
Backup based solutions require that the cluster on the secondary database has the same number of nodes as the cluster on the production database.
-
RTO (recovery time objective) is less than one hour.
-
RPO (recovery point objective) depends on the backup frequency – everything changed after the last backup is lost.
A backup based solution can be configured in several ways:
1. Test environment as standby
The production database is deployed in data center 1 (DC 1), and a test database is deployed on a separate cluster with the exact same number of nodes in data center 2 (DC 2). If DC 1 has an outage, the test database is removed and the production database is restored from backup in DC 2.
Backups of the production database can additionally be written to an archive volume or an external backup server in DC 2.
2. Remote mirroring
The backups of the production database in DC 1 are mirrored by the backup storage layer to a remote archive volume in DC 2. The mirroring is transparent to the backup process on the production database. The backup storage in DC 2 cannot be used while the remote mirroring is in progress.
The mirroring solution must be provided by the backup storage vendor, it is not implemented in Exasol.
3. Stretched archive
The archive volume of the production database is stretched across both data centers (DC 1 and DC 2), while the data volume remains local to DC 1. The archive volume in DC 2 cannot be used while mirroring is in progress.
This solution is fully implemented in Exasol and does not require any external services.
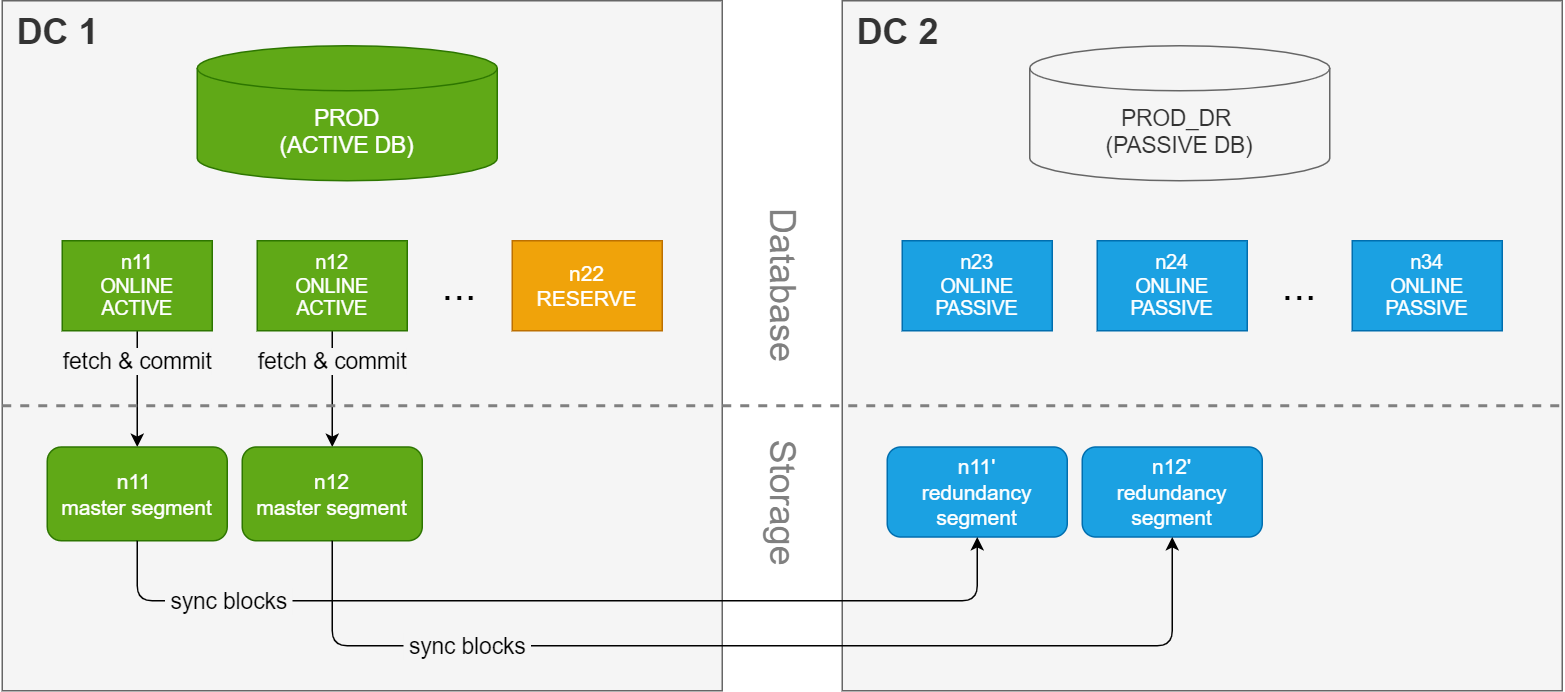
Synchronous dual data center
A synchronous dual data center (SDDC) solution stretches
a single cluster across two separate sites (data centers). Each data center has a database instance with the exact same number of nodes. Because the instances share the same data volume, only one of the instances can be running at a time. The production database is normally running on the primary (active) site, and data blocks in the master segments on the primary site are mirrored to redundancy segments on the secondary (passive) site.
This solution is more complex to setup and manage, but can provide business continuity with minimum downtime in case of a node failure or a complete outage on the primary site.
To learn more about how to plan, install, and administer an SDDC solution with Exasol, see Synchronous dual data center (SDDC) administration in the documentation for the latest version of Exasol.
Comparison of solutions
This table shows the main advantages and drawbacks of different dual data center solutions and how they affect RTO (recovery point objective) and RPO (recovery time objective). To learn more about the RTO and RPO concepts, see Terminology and timeline.
| Solution | RTO | RPO | Advantages | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ETL based |
~1 h |
significant |
Second database can be used autonomously Sites can have different cluster configurations |
The appropriate ETL mechanism must be developed and maintained |
|
Test environment as standby |
~1 h |
significant |
Second site can be used for testing |
Additional backups must be taken to the second site |
|
Remote mirroring |
~1 h |
significant |
Backup methods used on production can be used as before |
Storage vendor technology may lead to additional costs |
|
Stretched archive |
~1 h |
significant |
Backup methods used on production can be used as before Uses Exasol technology, no additional cost |
Quality of network connection between sites can impact backup performance |
|
Synchronous dual data center |
~60s |
none |
Minimal downtime without data loss |
Performance impact on the production database is proportional to the distance to the second site |