Network
This article provides an overview of the network infrastructure in an Exasol deployment.
An Exasol cluster is normally configured with two networks using separate physical interfaces: a private network for internal communication between the nodes in the cluster, and a public network that allows connections to the database from outside of the cluster. In a development scenario, you can use the same IP addresses for both networks, although this will result in low performance. For a production environment and for performance testing, always use separate networks.
In addition to the private and public networks, the cluster nodes can be connected by a separate interface for out-of-band management. It is also possible to have additional networks for purposes of fail safety or link bonding. For more information, see Setup Additional Networks (optional).
For more information about the network setup that will cover the performance requirements of most customers, refer to the Minimum Network Setup section.
Private network
The nodes in a cluster communicate over the private network. The private network is used to boot and configure nodes, to constantly exchange vitality and configuration information, and to synchronize the database payload.
The private network is managed through the cluster administration interface. IP addresses are assigned automatically through cluster-internal DHCP from a reserved, fixed address space.
Each private network must be fully separated from other networks. No traffic must pass in or out, and only the dedicated interfaces of the cluster nodes must be wired to this network. A cluster must never exchange traffic with private networks of other clusters.
The nodes must be directly connected to the layer 2 network (VLAN) and traffic must not be filtered.
Public network
You can configure a public network to allow access to the deployment from outside of the private network. Public networks are used by clients outside of the cluster to access the database instances and the administration interfaces.
The public IP addresses for a cluster must belong to the same network subnet. Clusters may share a public network as long as the IP addresses differ.
If the servers are equipped with out-of-band management interfaces, it is easiest to make them available from the public network (layer 3) and to integrate them in the EXAoperation web interface of the cluster.
If you plan to use EXA2EXA to load data from one database to another, you also require a connection string that is consecutive. In this case, IP addresses for a cluster must be assigned consecutively and without gaps.
Example:
10.1.50.10 = license server
10.1.50.11 = db node 1
10.1.50.12 = db node 2
10.1.50.13 = db node 3
Typical network setup
The following example shows a typical network setup:
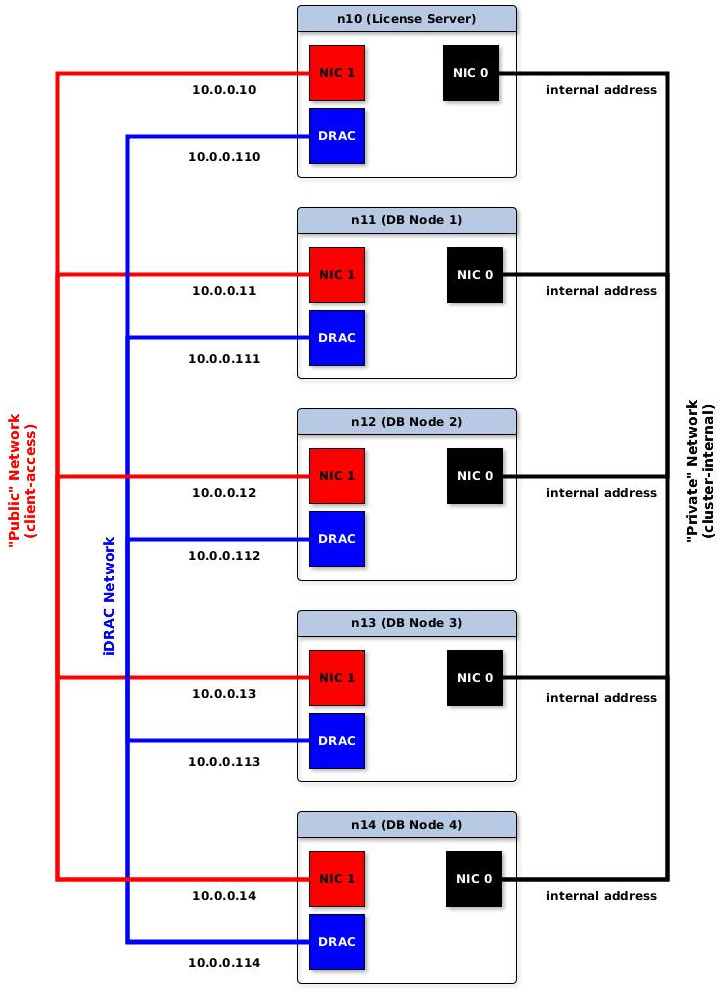
In this example, each node has three network interfaces: private network, public network, and a network for out-of-band management (in this case, iDRAC).
For more detailed information on preparing the network for Exasol, refer to the Prepare the Environment section in the Installation Guide.
